Thursday, September 16, 2010
idya
It's a sobering fact that a full 40 percent of the world's population—some 2.6 billion people—lack regular access to a toilet. Add to that the fact that one child dies every 15 seconds from water contamination, and it's not hard to see the motivation behind the Peepoo bag.
One of the UN Millennium Development Goals, set in 2000, is to halve by 2015 the proportion of people without sustainable access to drinking water and sanitation, but so far progress has been minimal. With that in mind, Swedish Peepoople created the Peepoo bag to serve as a personal, portable and low-cost latrine for all the many people who don't have one. Designed for use sitting, squatting or standing, the single-use, biodegradable plastic bag measures 14 by 38 cm and is lined with a urea-coated gauze layer that disinfects all waste. Used bags are odour-free for at least 24 hours and are safe for burial underground. Within two to four weeks after use, however, their contents get converted to high-quality fertiliser—something that's also rare in many areas and so could become a source of income and further enrichment for an individual or village. Following field tests last year in Kenya and India, the Peepoo bag is scheduled to begin production this summer.
Along with such efforts as distributing free insect nets to children in malaria-ridden areas and abolishing fees for school uniforms in poor countries, the Peepoo bag qualifies as a quick-win project that could rapidly improve the lives of many people. One to get in on, help out with, or be inspired by!
Wednesday, September 15, 2010
air cars
AIR CAR
We do it every day without thinking. Start the engine, drive around, fill up with fuel, pay a lot of money and pollute the atmosphere some more! But, it doesn’t have to be that way, many alternative sources of fuel are being developed.
Science fiction novelist Jules Verne had predicted that cars would one day run on air. Guess what the future of fuel is? You guessed it right, its air! Think about a car that runs on air. The air we breathe, the air that is for free. Imagine, it costs nothing to fill up your car with gas, and that gas also happens to be the same gas that fills our lungs with every breath!
The future of transportation will soon be whooshing down the road in the form of an unparalleled “green” earth- friendly technology that everyone will want to get their hands on as soon as they can: The Air Car. It is hard to believe that compressed air can be used to drive vehicles. However that is true and the “air car”, as it is popularly known, has caught the attention of researchers worldwide.
The topic air car can be made a project by making a demo model of the air car engine. The working of the engine can be better understood from the following videos
video.1(air car)
video.2(air car)
How does the Air car work?
Actually all engines work with compressed air. Most engines suck it in, heat it up, it pressurizes and it pushes on a piston. In an air car we pressurize the air first, so when we apply it to the piston, the piston is pushed. The idea is as simple as that
this aircar can be done as a project
make money with your website
Tuesday, September 14, 2010
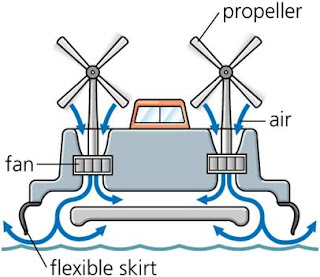
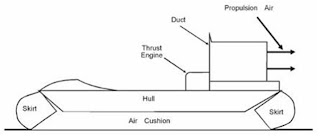
Working model of Hovercraft
- Can be powered by one or more engines
- Small crafts have a single engine with the drive split through a gear box
- Usually one engine drives the fan responsible for lifting the vehicle
- The other forces air from
- A skirt is required to quarantine airflow
- No contact with ground hence friction is eliminated
- The shape of the body affects stability
- All parts are essential for proper working
air cars
We do it every day without thinking. Start the engine, drive around, fill up with fuel, pay a lot of money and pollute the atmosphere some more! But, it doesn’t have to be that way, many alternative sources of fuel are being developed.
this aircar can be done as a project
mobilephone
A mobile phone allows its user to make and receive telephone calls to and from the public telephone network which includes other mobiles and fixed line phones across the world. It does this by connecting to a cellular network owned by a mobile network operator. A key feature of the cellular network is that it enables seamless telephone calls even when the user is moving around wide areas via a process known as handoff or handover.
In addition to being a telephone, modern mobile phones also support many additional services, and accessories, such as SMS (or text) messages, email, Internet access, gaming, Bluetooth, infrared, camera, MMS messaging, MP3 player, radio and GPS. Low-end mobile phones are often referred to as feature phones, whereas high-end mobile phones that offer more advanced computing ability are referred to as smartphones.
The first handheld cellular phone was demonstrated by Martin Cooper of Motorola in 1973, using a handset weighing in at two kilos.[2] In the year 1990, 12.4 million people worldwide had cellular subscriptions.[3] By the end of 2009, only 20 years later, the number of mobile cellular subscriptions worldwide reached approximately 4.6 billion, 370 times the 1990 number, penetrating the developing economies and reaching the bottom of the economic pyramid
nokia x6-16GB
| nokia x6-16GB specifications PRIZE Rs16499 | ||||
| OVERVIEW | a touch-screen phone perfect for entertainment and social networking | |||
| GENERAL | 2G network: gsm850/900/1800/1900 | |||
| 3G network: hsdpa900/1900/2100-excl.lat.america | ||||
| hsdpa850/1900/2100-usa | ||||
| status:released 2010,february&available | available colours black&black | |||
| SIZE | dimensions:111*51*13.8mm | |||
| weight: 122g | ||||
| DISPLAY | size:3.2" | |||
| capacitive touch screen | ||||
| resolution:640*360 pixes(nHD) | ||||
| up to 16.7 million colours | ||||
| automatic orientation sensor for display rotation | ||||
| 16:9 widescreen aspect ratio | ||||
| CAMERA | primary: 5MP, 2592*1944 pixels,carl zeiss optics, | |||
| autofocus,dual led flash,video light | ||||
| features: geo-tagging | ||||
| video: yes,vga@30fps | ||||
| secondary: yes,qcif@15fps | ||||
| MEMORY | phonebook:unlimited entries and fields,photocalls | |||
| call records: max 30 days | ||||
| internal:16GB storage,128MB RAM | ||||
| external: no card slot | ||||
| NETWORK AND CONNECTIVITY | gprs: class 32 | |||
| 3g network: hsdpa,3.6mbps | ||||
| wlan: wi-fi 802.11b/g,upnp | ||||
| stereo bluetooth version 2.1 with enhanced data rate | ||||
| high-speed usb 2.0 (micro usb connector) | ||||
| usb-charging | ||||
| support for pc synchronisation with nokia ovi suite | ||||
| SOFTWARE AND APPLICATIONS | :s60 5th edition | |||
| :symbion os version 9.4 | ||||
| :java midp 2.0 | ||||
| :flash lite 3.0 | ||||
| :contacts bar | ||||
| :open-source software(oss)web browser | ||||
| :playlist DJ | ||||
| :ovi music & maps3.0 | ||||
| :image&video editor | ||||
| :more applications from ovi store | ||||
| MUSIC AND AUDIO | :nseries digital music player | |||
| :playlist&grapical equaliser | ||||
| :bass booster,stereo widening&loudness | ||||
| :mp3,spmidi,aac,aac+,eaac+,wma | ||||
| POWER | BL-5J 1320 MAH LI-ION BATTERY | |||
| talk time: gsm up to 11h30min&wcdma up to 6h | ||||
| standby time:gsm up to 420 hours&wcdma up to 450 hours | ||||
| video playback time: up to 4 hours 30 mins | ||||
| music playback time: up to 35 hours | ||||
| ADDITIONAL FEATURES | :games | |||
| :radio | ||||
| :music | ||||
| :more additional applications from ovi store | ||||